Prisoners Dilemma Game Theory | The prisoner's dilemma is one of the most cited examples in the field of game theory, and in the academic studies of economics and international relations. The prisoner's dilemma is a fundamental exercise in game theory and serves as a great catalyst for discussions about decision making, communications, ethics and responsibility. Like many of the things we've been talking about in this entire course, it's a much larger subject than we. First published thu sep 4, 1997; It discusses the concept of nash equilibrium and introduces the. What game are you playing? A prisoner's dilemma is a situation where individual decision makers always have an incentive to choose in a way that creates a less than optimal outcome for the individuals as a group. Game theory of cheating firms. Multiplayer iterated prisoner's dilemma simulates the evolution of cooperation or defection among several common strategies based on initial populations. Tucker, who developed it from earlier works. In addition, the prisoner's dilemma has been used to help understand economic, politics, elections, crime, as well as behavior in business. First, the classic example of the prisoner's dilemma from wikipedia Substantive revision tue apr 2, 2019. Nicknamed in 1950 by albert w. The pd with replicas and causal decision theory. The prisoners' dilemma is a classic example of a game which involves two suspects, say p and q, arrested by. This video introduces game theory and goes through an example of the prisoners' dilemma. Java applets, online simulations, and game theory demonstrations. Multiplayer iterated prisoner's dilemma simulates the evolution of cooperation or defection among several common strategies based on initial populations. In the fomer, the prisoner's dilemma game is played repeatedly, opening the possibility that a player can use its current move to reward or punish the 7. Game theory first emerged in 1944 in a book written by john von neumann and oskar mogenstern. The prisoner's dilemma is a fundamental exercise in game theory and serves as a great catalyst for discussions about decision making, communications, ethics and responsibility. The prisoner's dilemma is a standard example of a game analyzed in game theory that shows why two completely rational individuals might not cooperate. The us and the soviet union have nuclear weapons (i.e., they're the prisoners facing the dilemma). Game theory of cheating firms. Classical prisoner's dilemma game simulation. A prisoner's dilemma is a situation where individual decision makers always have an incentive to choose in a way that creates a less than optimal outcome for the individuals as a group. A prisoners' dilemma refers to a type of economic game in which the nash equilibrium is such that both players are worse off even though they both select their optimal strategies. The pd with replicas and causal decision theory. Assessment | biopsychology | comparative | cognitive | developmental | language | individual differences | personality | philosophy | social | methods | statistics | clinical | educational | industrial | professional items | world psychology |. Rat out another for personal benefit, or cooperate? Its purpose is to investigate whatever aspects i found to be related to the prisoner's. One area of inquiry in game theory is in finding ways around this dilemma. The game commonly referred to as the prisoner's dilemma is a classic example used to demonstrate game theory. The game is usually phrased in terms of two suspects, both of whom have been arrested. Should one cooperate or betray? This is what's called a prisoner's dilemma game. This is the dilemma both the prisoner's face. When one starts to study game theory, a game called prisoner's dilemma is one of the first examples to be introduced. The prisoner's dilemma is a problem in game theory in which two competing players end up in a worse situation because they assume the other one won't cooperate. It demonstrates how communication between the participants can drastically alter their best strategy. Using game theory, researchers modeled two ways of prioritizing vaccinations, to see which saved more lives. The prisoner's dilemma is one of the most cited examples in the field of game theory, and in the academic studies of economics and international relations. The prisoner's dilemma is a problem in game theory in which two competing players end up in a worse situation because they assume the other one won't cooperate. It was originally framed by merrill flood and melvin dresher while working at rand in 1950. This is the dilemma both the prisoner's face. Multiplayer iterated prisoner's dilemma simulates the evolution of cooperation or defection among several common strategies based on initial populations. The traditional prisoners dilemma works as follows, you and your accomplice get caught committing a while this may not apply to markets (necessarily) the prisoners dilemma and game theory have a wide ranging impact on social constructs and every. Either party is given the. The police have captured two criminals and are interrogating them in separate rooms, so they can't communicate with each other. Game theory worked example from ap microeconomics. Like many of the things we've been talking about in this entire course, it's a much larger subject than we. In this classic game theory experiment, you must decide: Foundational essentially confess both confess both confess you will both get three years you will both get three years so this scenario is called the prisoner's dilemma because. Positive numbers represent good outcomes, negative. One area of inquiry in game theory is in finding ways around this dilemma. Its use has transcended economics, being used in fields such as business management, psychology or biology, to name a few. Should one cooperate or betray? It is usually explained through the use of this story.
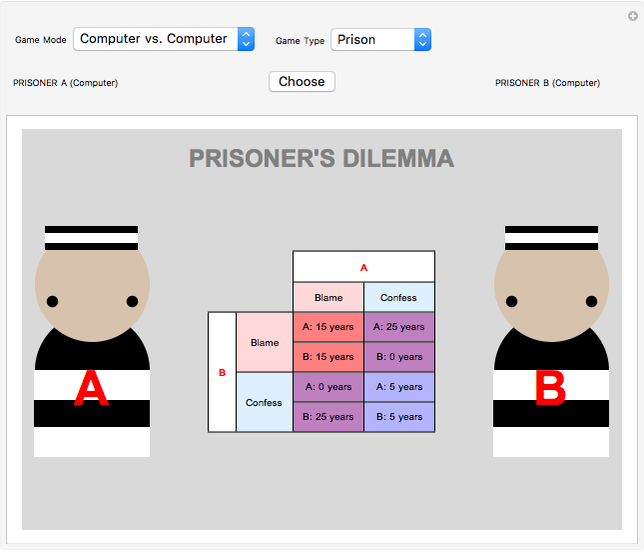

The prisoner's dilemma is probably the most widely used game in game theory prisoners dilemma. This is the dilemma both the prisoner's face.
Prisoners Dilemma Game Theory: The police have lacking proof for a conviction and the game helped students understand how negotiation matters in business.
0 comments:
Post a Comment